OM301
WESTERN DIAGNOSIS
WESTERN DIAGNOSIS
Introduction
History Taking
Vital Signs
Head, Neck
Thorax and Lungs
Cardiovascular
1 | Sep. 9 | An Overview History Taking |
2 | Sep. 16 | Physical Examination - General Survey and Vital Signs |
3 | Sep. 23 | Physical examination - The Head, Neck |
4 | Sep. 30 | Holiday |
5 | Oct. 7 | Physical examination - Thorax and Lungs |
6 | Oct. 14 | Physical examination - The Cardiovascular System |
7 | Oct. 21 | Midterm(90mins) Review |
8 | Oct. 28 | Physical examination - The Breasts and Axillae |
9 | Nov.4 | Physical examination - The Abdomen |
10 | Nov. 11 | Holiday |
11 | Nov. 18 | Physical examination- Nerve Systems |
12 | Nov. 25 | Physical examination - The Peripheral Vascular System |
13 | Dec. 2 | Physical examination- The Musculoskeletal System |
14 | Dec. 9 | Practice in person |
15 | Dec. 16 | Final exam (90mins) Review |
Western Medicine Diagnosis Introduction
BASIC PHYSICAL DIAGNOSIS
A road map to clinical proficiency in three critical areas:
◦The health history
◦The physical examination
◦The written record
General data -Name, gender, age, phone, occupation, marital status
🞂Date and Time of History.
The date is always important. You are strongly advised to routinely document the time you evaluate the patient, especially in urgent, emergent, or hospital settings.
History Taking
Symptom:
Symptoms are subjective and experienced only by the patient.
For example, pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and a rash are all symptoms. They’re the feelings, sensations, and changes in health that a person notices.
Signs:
A sign is objective evidence of disease that another person can detect, often a healthcare professional. For example, a doctor might observe a rash, a swollen joint, or a fever when examining a patient.
THE HEALTH HISTORY: STRUCTURE AND PURPOSES
🞂Chief Complaint(s)
🞂Present Illness
🞂Past History
🞂Family History,
🞂Personal and Social History
🞂Review of Systems
Chief complaint:
The one or more symptoms or concerns causing the patient to seek care
🞂Make every attempt to quote the patient’s own words.
🞂For example, “My stomach hurts and I feel awful.” Sometimes patients have no overt complaints, in which case you should report their goals instead. For example, “I have come for my regular checkup”; or “I’ve been admitted for a thorough evaluation of my heart.”
History of present illness
- Amplifies the Chief Complaint, describes how each symptom developed
Includes patient’s thoughts and feelings about the illness.
- This section of the history is a complete, clear, and chronologic account of the problems prompting the patient to seek care.
- The narrative should include the onset of the problem, the setting in which it has developed, its manifestations, and any treatments.
- The principal symptoms should be well-characterized, with descriptions of
- (1) location
- (2) quality
- (3) quantity(amount) or severity
- (4) timing, including onset, duration, and frequency
- (5) the setting in which they occur
- (6) factors that have aggravated or relieved the symptoms
- (7) associated manifestations
Past History
Childhood Illnesses:
- such as measles, rubella风疹 , mumps, whooping cough, chicken pox, rheumatic fever, scarlet fever, and polio are included in the Past History.
- Also included are any chronic childhood illnesses.
Adult Illnesses in each of four areas:
- Medical (such as diabetes, hypertension, hepatitis, asthma, HIV disease, information about hospitalizations);
- Surgical (include dates, indications, and types of operations);
- Obstetric/gynecologic (relate obstetric history, menstrual history, birth control, and sexual function);
- Psychiatric (include dates, diagnoses, hospitalizations, and treatments).
Family History
- Outline or diagram the age and health, or age and cause of death, of each immediate relative, including parents, grandparents, sib-lings(sisters, brothers), children, and grandchildren.
- Review each of the following conditions and record if they are present or absent in the family: hypertension, coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, thyroid or renal disease, cancer (specify type), arthritis, tuberculosis, asthma or lung disease, headache, seizure disorder, mental illness, suicide, alcohol or drug addiction, and allergies, as well as symptoms reported by the patient.
Personal and Social History
- occupation;
- home situation and significant others; sources of stress, both recent and long-term; important life experiences, job history, financial situation, and retirement;
- lifestyle habits that promote health or create risk such as exercise and diet, dietary supplements or restrictions, and use of coffee, tea, and other caffeine-containing beverages.
- You may want to include any alternative health care practices.
Review of Systems
- Think about asking series of questions going from “head to toe.”
- Start with a fairly general question as you address each of the different systems. This focuses the patient’s attention and allows you to shift to more specific questions about systems that may be of concern. Examples of starting questions are: “How are your ears and hearing?” “How about your lungs and breathing?” “Any trouble with your heart?” “How is your digestion?” “How about your bowels?”
- Keep your technique flexible.
General.
- Usual weight, recent weight change, any clothes that fit more tightly or loosely than before. Weakness, fatigue, fever.
- Skin. Rashes, lumps, sores, itching, dryness, color change, changes in hair or nails.
- Head: Headache, head injury, dizziness, lightheadedness.
- Eyes: Vision, glasses or contact lenses, last examination, pain, redness, excessive tearing, double vision, blurred vision, spots, specks, flashing lights, glaucoma, cataracts.
- Ears: Hearing, tinnitus, vertigo, earaches, infection, discharge. If hearing is decreased, use or nonuse of hearing aids.
- Nose and sinuses: Frequent colds, nasal stuffiness, discharge, or itching, hay fever, nosebleeds, sinus trouble.
- Throat (or mouth and pharynx): Condition of teeth, gums, bleeding gums, dentures, if any, and how they fit, last dental examination, sore tongue, dry mouth, frequent sore throats, hoarseness.
- Neck. Lumps, “swollen glands,” goiter, pain, or stiffness in the neck.
Breasts. Lumps, pain or discomfort, nipple discharge, self-examination practices.
- Respiratory. Cough, sputum (color, quantity), hemoptysis, dyspnea, wheezing, pleurisy, last chest x-ray. You may wish to include asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
- Cardiovascular. Heart trouble, high blood pressure, heart murmurs, chest pain or discomfort, palpitations, dyspnea, edema, past electrocardiographic or other heart test results.
- Gastrointestinal.
- Trouble swallowing, heartburn, appetite, nausea, bowel movements, color and size of stools, change in bowel habits, rectal bleeding or black stools, hemorrhoids, constipation, diarrhea. Abdominal pain, food intolerance, excessive belching or passing of gas. Jaundice, liver or gallbladder trouble, hepatitis.
- Urinary. Frequency of urination, polyuria, nocturia, urgency, burning or pain on urination, hematuria, urinary infections, kidney stones, incontinence
- Genital.
- Male: Hernias, discharge from or sores on the penis, testicular pain or masses, history of sexually transmitted diseases and their treatments. Sexual habits, interest, function, satisfaction, Exposure to HIV infection.
- Female: Age at menarche; regularity, frequency, and duration of periods; amount of bleeding, bleeding between periods, last menstrual period; dysmenorrhea, PMS; age at menopause, menopausal symptoms, postmenopausal bleeding. Vaginal discharge, itching, sores. Number of pregnancies, number and type of deliveries, number of abortions (spontaneous and induced); complications of pregnancy; birth control methods. Exposure to HIV infection.
- Peripheral Vascular. leg cramps, varicose veins, past clots in the veins.
- Musculoskeletal.
- Muscle or joint pains, stiffness, arthritis, gout, and backache.
- If present, describe location of affected joints or muscles, presence of any swelling, redness, pain, tenderness, stiffness, weakness, or limitation of motion or activity; include timing of symptoms (for example, morning or evening), duration, and any history of trauma.
- Neurologic.
- Fainting, seizures, weakness, paralysis, numbness or loss of sensation, tingling or “pins and needles,” tremors or other involuntary movements.
- Hematologic.
- Anemia, easy bruising or bleeding, past transfusions and/or transfusion reactions.
- Endocrine.
- Thyroid trouble, heat or cold intolerance, excessive sweating, excessive thirst or hunger, polyuria.
Physical examination technique
- Inspection
- Palpation
- Light palpation
- Deep palpation
- Percussion
- direct percussion
- indirect percussion
- Auscultation (stethophone/stethoscope)
GENERAL EXAMINATION.
I. The General condition of the patient.
II. The skin and the subcutaneous cellular tissue.
III. lymph nodes
I. The General Condition of the Patient.
- Vital sign: Blood Pressure, Pulse (HR), Respiration, Temperature
- Development (Height, Build, Weight)
- State of nutrition
- Consciousness
- Tone
- Facial Expression
- The position in bed (Active position, Passive position, Compulsive position)
- Posture and gait.
Vital sign:
BLOOD PRESSURE: blood pressure is considered to be between 90/60mmHg and 120/80mmHg. high blood pressure is considered to be 140/90mmHg or higher. low blood pressure is considered to be below 90/60mmHg.
HEART RATE AND RHYTHM:
The radial pulse is commonly used to assess the heart rate. If the rhythm is regular and the rate seems normal, count the rate for 15 seconds and multiply by 4.
Normally, adults heart rate is 60 - 100.
RESPIRATORY RATE AND RHYTHM:
Observe the rate, rhythm, depth, and effort of breathing.
Count the number of respirations in 1 minute either by visual inspection or by subtly listening over the patient’s trachea with your stethoscope during your examination of the head and neck or chest.
Normally, adults take 14 to 20 breaths a minute in a quiet regular pattern.
TEMPERATURE:
The average oral temperature, at 37°C (98.6°F), In the early morning hours it may fall as low as 35.8°C (96.4°F), and in the late afternoon or evening it may rise as high as 37.3°C (99.1°F).
Rectal temperatures are higher than oral temperatures by an average of 0.4 to 0.5°C (0.7 to 0.9°F).
Axillary temperatures are lower than oral temperatures by approximately 1 degree, but take 5 to 10 minutes to register and are generally considered less accurate than other measurements.)
Fever:
(Normal: 36~37℃)
Pathogeny:
1. infective fever
2. noninfective fever: absorption fever, immunological reaction, endocrine system illness, skin illness, nerve centre fever.
Degree:
Low fever: 37.3~38℃
Middle fever: 38.1~39℃
High fever: 39.1~41℃
Extra high fever: over 41℃
2. Development (Height, Build, Weight):
Height
Weight
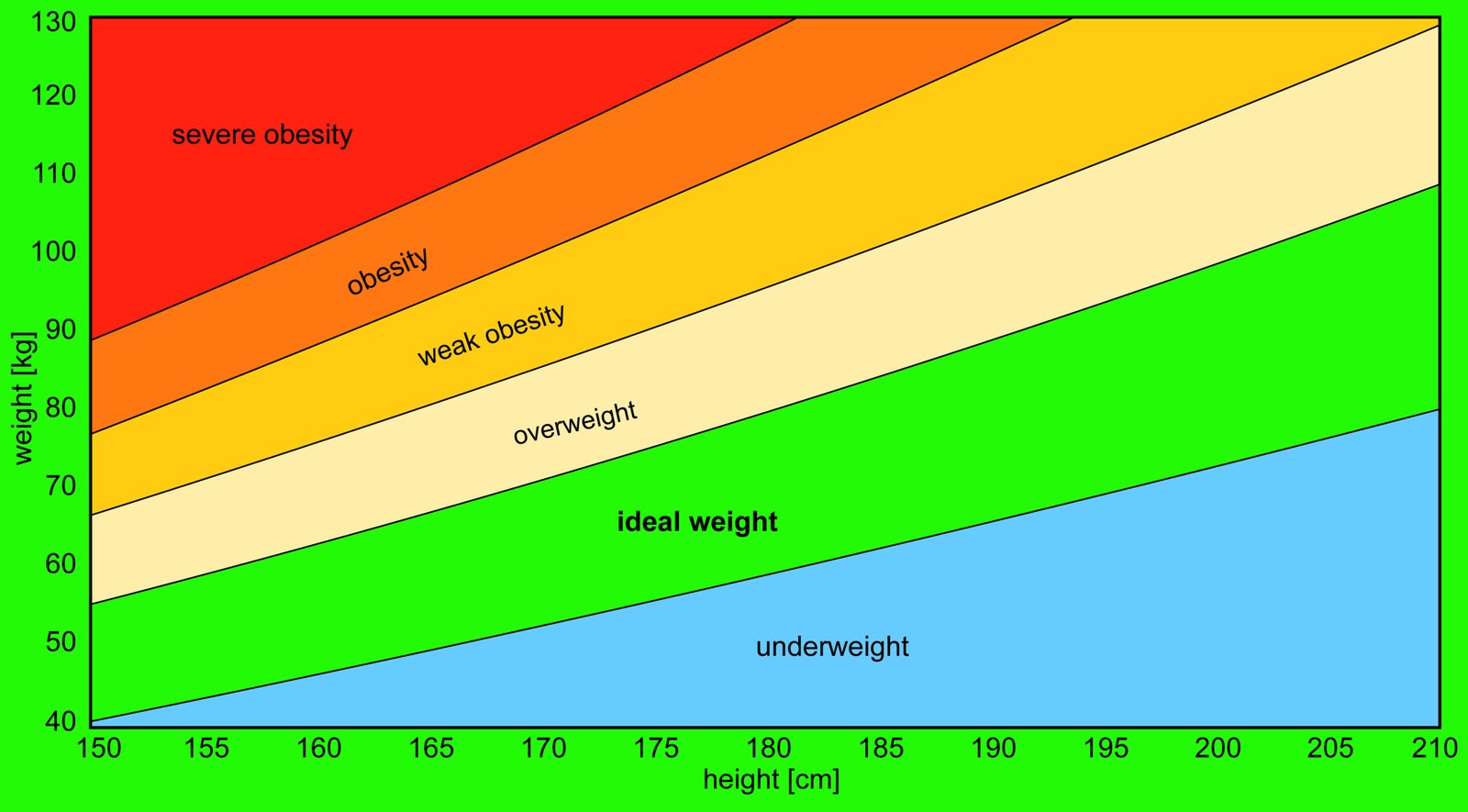
3. State of nutrition:
The nutritional status of the patient based on height and weight is interpreted by the body mass index (BMI)
BMI = weight (pounds)/height (inches)2 × 703
BMI less than 18.5 kg/m2 underweight;
BMI between 18.5 and 25 healthy weight;
BMI between 25.1 and 29.9 overweight;
BMI of 30 or more is considered obese.
4. Consciousness
5. Tone of Voice
6. Facial Expression
7. The position in bed (Active position,Passive position,Compulsive position)
8. Posture and gait.
II The skin and the subcutaneous cellular tissue.
Skin color
Moisture
Elasticity
Skin eruption(Rashes)
Subcutaneous hemorrhage (skin bruise)
Spider angioma 蜘蛛痣
Edema
Subcutaneous nodules
Scar
Hair
III lymph nodes:
Normal: 0.2-0.5 cm, soft, not pain, smooth, not easy to find.
Looking for:
Location, size, number, soft or hard, pain, moving, red, swollen, scar, Looking primary illness.
Reason of lymph nodes enlarge:
Inflammation
Cancer
Blood System illness
HEAD EXAMINATION.
Hair and scalp (gloss, scurf, lose hair, lesions)
Skull (Shape, head circumference, fontanel)
Face and orifices
Eye
Nose
Ear
Mouth
Tongue
Teeth
Gum
Pharynx (throat)
Inspection
Inspect the position of the head. Does the patient hold the head erect?
Is there any asymmetry of the facial structure?
Is the head in proportion to the rest of the body?
Inspect the scalp for lesions. Describe the hair.
Are any masses present? If so, describe their size, consistency, and symmetry.
Visual Fields
Assess Fields by Confrontation Testing
The examiner stands or sits 3 feet in front of and at eye level with the patient.
The patient is asked to close the right eye while the examiner closes his or her own left eye, each fixating on the other’s nose.
The examiner holds up fists with the palms facing him or her.
The examiner then shows one or two fingers on each hand simultaneously and asks the patient how many fingers he or she sees.
The hands are moved from the upper to the lower quadrants, and the examination is repeated. The examination is then repeated, with the other eye of the patient and that of examiner. The fingers should be seen by both patient and examiner simultaneously.
CONVERGENCE
Ask the patient to follow your finger or pencil as you move it in toward the bridge of the nose. The converging eyes normally follow the object to within 5 cm to 8 cm of the nose.
Swinging Flashlight Test
In dim room light, note the size of the pupils.
After asking the patient to gaze into the distance, swing the beam of a penlight back and forth from one pupil to the other, each time concentrating on the pupillary size and reaction in the eye that is lit.
sinuses
Palpate for sinus tenderness. Press up on the frontal sinuses from under the bony brows, avoiding pressure on the eyes. Then press up on the maxillary sinuses.
NECK EXAMINATION.
- Skin and Nodules(mass), Neck stiffness
- Blood Vessels – external jugular vein
Sit or stand couldn’t see, lie down < 2/3 from clavicle to angle of the jaw
- Thyroid
- NECK EXAMINATION - Palpation
Palpation confirms the information obtained by inspection. The patient’s head should be slightly flexed and cradled in the examiner’s hands.
Palpate the Thyroid Gland
There are two approaches to palpating the thyroid gland.
The posterior approach the examiner should stand behind the patient to palpate the thyroid by the posterior approach. In this approach, the examiner places two hands around the patient’s neck, which is slightly extended. The examiner uses the left hand to push thetrachea to the right. The patient is asked to swallow while the examiner’s right hand rolls over
the thyroid cartilage. As the patient swallows, the examiner’s right hand feels for the thyroid gland against the right sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Palpate for Supraclavicular Nodes- Palpation for supraclavicular nodes concludes the examination of the head and neck. The examiner stands behind the patient and places the fingers into the medial supraclavicular fossae, deep to the clavicle and adjacent to the sternocleidomastoid muscles. The patient is instructed to take a deep breath while the examiner presses deeply in and behind the clavicles.
- Any supraclavicular nodes that are enlarged are palpated as the patient inspires.
Common or Concerning Symptoms
- Headache
- Change in vision
- Double vision
- Hearing loss, earache, tinnitus
- Vertigo
- Nosebleed,
- Sore throat, hoarseness
- Swollen glands
- Goiter
CHEST EXAMINATION.
Surface symbol:
suprasternal notch
sternal angle
infrasternal angle
supraclavicular fossa
suprascapular region
infrascapular region
costal spinal angle
Examination of the Anterior Chest
INSPECTION
Observe the shape of the patient’s chest and the movement of the chest wall.
Deformities or asymmetry
Abnormal retraction of the lower interspaces during inspiration
Local lag or impairment in respiratory movement
PALPATION
Identification of tender areas
Assessment of observed abnormalities
Further assessment of chest expansion. Place your thumbs along each costal margin, your hands along the lateral rib cage. As you position your hands, slide them medially a bit to raise loose skin folds between your thumbs. Ask the patient to inhale deeply. Observe how far your thumbs diverge as the thorax expands, and feel for the extent and symmetry of respiratory movement.
Examination of the Posterior Chest
INSPECTION
From a midline position behind the patient, note the shape of the chest and the way in which it moves, including: Deformities or asymmetry
Abnormal retraction of the interspaces during inspiration. Retraction is most apparent in the lower interspaces. Supraclavicular retraction is often associated.
Impaired respiratory movement on one or both sides or a unilateral lag (or delay) in movement.
PALPATION
As you palpate the chest, focus on areas of tenderness and abnormalities in the overlying skin, respiratory expansion, and fremitus.
Identify tender areas. Carefully palpate any area where pain has been reported or where lesions or bruises are evident.
Test chest expansion. Place your thumbs at about the level of the 10th ribs, with your fingers loosely grasping and parallel to the lateral rib cage. As you position your hands, slide them medially just enough to raise a loose fold of skin on each side between your thumb and the spine.
Ask the patient to inhale deeply. Watch the distance between your thumbs as they move apart during inspiration, and feel for the range and symmetry of the rib cage as it expands and contracts.
Feel for tactile fremitus.
Fremitus refers to the palpable vibrations transmitted through the bronchopulmonary tree to the chest wall when the patient speaks.
LUNG EXAMINATION
Inspection
respiratory movement
breathing rate
respiratory rhythm
Palpation
thoracic expansion
vocal fremitus
Percussion
Normal lung ---Resonant
(upper bound 2-3cm over clavicle bone, lower bound in the 6th intercostal space in mid clavicle line)
Illness
Consolidation ---Dull
Pneumothorax ---Hyper resonant
Auscultation
Normal breath sound
bronchial breath sound
bronchovesicrllar breath sound
Vesicular
Adventitious sound
Crackles (moist rales)
Wheezes
Rhonchi
HEART EXAMINATION
Inspection and Palpation
The Apex-beat
5th intercostal space, 0.5-1 cm in the middle side of midclavicular line, scope diameter 2.0-2.5cm
Alteration in the Width and Strength of the Apex-beat
The Neighborhood of the Heart in general
Percussion
1. Normal Percussion Figure of the Heart.
Right boundary (cm) | Intercostal space | Left boundary (cm) |
2-3 | II | 2-3 |
2-3 | III | 3.5-4.5 |
3-4 | IV | 5-6 |
V | 7-9 | |
It is about 8-10 cm from midline to Left midclavicular line | ||
2. Enlargement of the Area of Heart-dullness (Hypertrophy and dilatation of the left ventricle, Fluid in the pericardium)
3. Diminution or Loss of Heart-dullness (emphysema of the lungs, pneumo-pericardium,
4. Displacement (dislocation) of the Heart-dullness
(chest flattened or pressed in, Emphysema of the lungs, pleurisy, Shrinking of the lungs)
Auscultation
1.Method
1.Aortic valve : 2d intercostal space, right of sternum.
2.Pulmonic valve : 2d intercostal space, left of sternum
3.Tricuspid valve :left sternal border, 4th intercostal space
4.Mitral valve : Apex
2. Normal Condition
The first and second heart-sounds
1st sound : Closure of the mitral and the tricuspid valves and ventricular contraction.
2d sound : Closure of aortic and pulmonary valve.
Breasts and Axillae
Abdomen
Nerve
Peripheral Vascular
Musculoskeletal
Pregnant Woman
The Breasts
The female breast lies against the anterior thoracic wall, extending from the clavicle and 2nd rib down to the 6th rib, and from the sternum across to the midaxillary line. The breast overlies the pectoralis major and at its inferior margin, the serratus anterior. The breast is hormonally sensitive tissue, responsive to the changes of monthly cycling and aging.
INSPECTION
Inspect the breasts and nipples with the patient in the sitting position A thorough examination of the breast includes careful inspection for skin changes, symmetry, contours(Shape), and retraction in four views— arms at sides, arms over head, arms pressed against hips, and leaning forward.
PALPATION
Palpation is best performed when the breast tissue is flattened. The patient should be supine. Plan to palpate a rectangular area extending from the clavicle to the inframammary fold or bra line, and from the midsternal line to the posterior axillary line and well into the axilla for the tail of the breast.
The Axillae
INSPECTION
Inspect the skin of each axilla, noting evidence of: Rash Infection Unusual pigmentation
PALPATION
To examine the left axilla, ask the patient to relax with the left arm down. Help by supporting the left wrist or hand with your left hand. Cup together the fingers of your right hand and reach as high as you can toward the apex of the axilla. Warn the patient that this may feel uncomfortable. Your fingers should lie directly behind the pectoral muscles, pointing toward the midclavicle. Now press your fingers in toward the chest wall and slide them downward, trying to feel the central nodes against the chest wall. Of the axillary nodes, these are the most often palpable. One or more soft, small (<1 cm), nontender nodes are frequently felt.
Breast Self Examination
Step 1: Look in the Mirror (Hands on Hips)
Stand in front of a mirror with your shoulders straight and hands on your hips.
Look for:
Usual size, shape, and color
Even shape with no swelling or changes
Tell your doctor if you see:
Skin dimpling or puckering
Nipple changes or pulling inward
Redness, rash, or swelling
Step 2: Raise Your Arms and Look Again
Raise your arms and check for the same changes as above.
Step 3: Check for Nipple Discharge
Look for any fluid coming from one or both nipples (clear, milky, yellow, or bloody).
Step 4: Feel for Lumps Lying Down
Lie down and use your right hand to feel your left breast, then your left hand to feel your right.
Use a circular motion with your finger pads
Cover the whole breast from top to bottom and side to side
Use light, medium, and firm pressure to feel all layers
Step 5: Feel for Lumps While Standing or Sitting
Check your breasts while standing or in the shower.
Use the same circular motion
Cover the entire breast area
Inspection
- Appearance
- Breathing movement
- Veins
- Gastral or intestinal pattern and peristalsis
Palpation:
Light Palpation.
- Feeling the abdomen gently is especially helpful in identifying abdominal tenderness, muscular resistance, and some superficial organs and masses. It also serves to reassure and relax the patient.
Deep Palpation.
This is usually required to delineate abdominal masses and enlarged organs.
Identify any masses and note their location, size, shape, consistency, tenderness, pulsations, and any mobility with respiration or with the examining hand.
- Abdominal guarding
- Tenderness and Rebound tenderness
- Organs : Liver, GB, Spleen, Kidney,
- Lumps
- McBurney’s Point (Appenicitis):
Pain in the right lower quadrant one third the distance from the anterior iliac crest to the umbilicus.
Caused by the inflamed appendix - Murphy’s sign (Cholecystitis): Pain on inspiration during gentle palpation below the right subcostal arch.As the patient breathes in, the liver moves down exposing the gallbladder to pressure from the examiners hand. Murpy’s sign may also be present with hepatitis.
3. Percussion
Liver
Stomach
Spleen
Kidney: Assessing Kidney Tenderness.
Shifting dullness
4. Auscultation:
Place the diaphragm of your stethoscope gently on the abdomen. Listen for bowel sounds and note their frequency and character. Listen to the abdomen before performing percussion or palpation, since these maneuvers may alter the frequency of bowel sounds.
1. Bowel sound normal 4-5/mins
a. Bowel sound active >10/mins
b. Hypoactive bowel sounds: < 1/ 2-5 mins
2. Vascular accentuated
3. Fetal heart sounds when pregnancy over 5 months 130-160/mins
Nerve Systems
- Important Areas of Examination
- Mental status: appearance and behavior, speech and language, mood, thoughts and perceptions, cognition
- Cranial Nerves I through XII
- I Smell
- II Visual acuity, visual fields
- III Pupillary reactions
- III, IV, VI Extraocular movements
- V Corneal reflexes, facial sensation, and jaw movements
- VII Facial movements
- VIII Hearing
- IX, X Swallowing and rise of the palate
- V, VII, X, XII Voice and speech
- XI Shoulder and neck movements
- XII Tongue symmetry and position
- Motor system: muscle bulk, tone, and strength; coordination, gait, and stance
- Motor function
- muscle strength
- muscular tension
- Involuntary movements
- Tremor
- Choreic movement (舞蹈病)
- Athetosis (手足徐动症)
- Motor function
- Sensory system: pain and temperature, position and vibration, light touch, discrimination
2. Sensory function- Superficial sensibility
- Pain sensation
- Touch sensation
- temperature sense
- Superficial sensibility
- Deep sensibility
- Movement sense
- Position sense
- Vibration sense
- Deep sensibility
- Deep tendon, abdominal, and plantar reflexes
3. Neural reflex- Superficial reflexes
- Abdominal reflex
- plantar reflex---Babinski
- Deep Reflexes
- biceps tendon reflex
- triceps tendon reflex
- patellar tendon reflex
- achilles tendon reflex
- Pathologic reflex: Babinski (central nerve damaged)
- Superficial reflexes
Common or Concerning Symptoms
- Pain in the arms or legs
- Intermittent claudication (跛行)
- Cold, numbness, pale in the arm, or legs, body hair loss
- Color change in fingertips or toes in cold weather
- Swelling in calves, legs, or feet
- Swelling with redness or tenderness
- Important Areas of Examination
- The Arms Size, symmetry, skin color, Radial pulse, brachial pulse
- TECHNIQUES OF EXAMINATION
- Assessment of the peripheral vascular system relies primarily on inspection of the arms and legs, palpation of the pulses, and a search for edema.
Arms
- Inspect both arms from the fingertips to the shoulders. Note: Their size, symmetry, and any swelling The venous pattern The color of the skin and nail beds and the texture of the skin
- Palpate the radial pulse with the pads of your fingers on the flexor surface of the wrist laterally. Partially flexing the patient’s wrist may help you feel this pulse. Compare the pulses in both arms.
The Legs
- Size, symmetry, skin color Femoral pulse and inguinal lymph nodes
- Popliteal, dorsalis pedis, and posterior tibial pulses
- Peripheral edema
If edema is present, look for possible causes in the peripheral vascular system.
These include
recent deep venous thrombosis,
chronic venous insufficiency due to previous deep venous thrombosis or to incompetence of the venous valves, and
lymphedema.
The Musculoskeletal System
- Important Areas of Examination for Each of the Major Joints
- Inspection for joint symmetry, alignment, bony deformities
- Inspection and palpation of surrounding tissues for skin changes, nodules, muscle atrophy,
- Range of motion and maneuvers to test joint function and stability,
- integrity of ligaments, tendons, bursae, especially if pain or trauma
- Assessment of inflammation or arthritis, especially swelling, warmth, tenderness, redness
The Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
To locate and palpate the joint, place the tips of your index fingers just in front of the tragus of each ear and ask the patient to open his or her mouth. The fingertips should drop into the joint spaces as the mouth opens. Check for smooth range of motion; note any swelling or tenderness.
The Shoulder
The Elbow
- Support the patient’s forearm with your opposite hand so the elbow is flexed to about 70°.
- Palpate the olecranon process and press on the epicondyles for tenderness.
- Note any displacement of the olecranon.
The Wrist and Hand
Palpate the eight carpal bones lying distal to the wrist joint, and then each
of the five metacarpals and the proximal, middle, and distal phalanges.
Palpate any other area where you suspect an abnormality.
SPINE
- Inspection
- Spine curvature
- Spinal mobility
- Palpation ---Tenderness
- Percussion---Percussion pain
The Pregnant Woman
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CHANFGS
During pregnancy, there are changes in the thyroid gland, breasts, abdomen, and pelvis. You may also detect minor skin changes such as the mask of pregnancy and abdominal striae. • During pregnancy, the thyroid gland and the breasts undergo moderate enlargement due to hormonal stimulation and increased vascularity and hyperplasia of glandular tissue. There may be tenderness and tingling in the breasts that makes them more sensitive during examination.
By the third month of gestation, the breasts become more nodular, requiring careful palpation to avoid discomfort as you examine for any breast masses. • The nipples become larger and more erectile. From mid to late pregnancy, colostrum, a thick, yellowish secretion rich in nutrients, may be expressed from the nipples. The areolae darken, and Montgomery’s glands are more prominent. The venous pattern over the breasts becomes increasingly visible as pregnancy progresses
The abdomen’s most notable change is distention, primarily from the increasing size of the growing uterus and fetus. • Early distention from fluid retention and relaxation of abdominal muscles may be noted before the uterus becomes an abdominal organ (12–14 weeks of pregnancy).
As the skin stretches to accommodate the growth of the fetus, purplish striae may appear. • The linea nigra(黑线), a brownish black pigmented line following the midline of the abdomen, may become evident. • Muscle tone is diminished as pregnancy advances, and separation of the rectus muscles at the midline of the abdomen, may be noticeable in the later trimesters of pregnancy.
TECHNIQUES OF EXAMINATION
Positioning.
• Positioning is important when examining the abdomen of a pregnant woman given the added time and attention needed to palpate the uterus and listen to the fetal heart. The semi-sitting position with the knees bent, affords the greatest comfort, as well as protection from the negative effects of the weight of the gravid uterus on abdominal organs and vessels.
Vital Signs and Weight
Take the blood pressure. A baseline reading helps to determine the woman’s usual range. In midpregnancy, blood pressure is normally lower than in the nonpregnant state. • Measure the weight. First-trimester weight loss related to nausea and vomiting is common but should not exceed 5 pounds.
General Inspection
Inspect the overall health, nutritional status, neuromuscular coordination, and emotional state as the woman walks into the exam room and climbs on the examination table.
• Face.
The mask of pregnancy, chloasma黄褐斑, is normal. It consists of irregular brownish patches around the eyes or across the bridge of the nose.
• Breasts Inspect the breasts and nipples for symmetry and color. The venous pattern may be marked, the nipples and areolae are dark, and Montgomery’s glands are prominent.
Abdomen
Position the pregnant woman in a semi-sitting position with her knees flexed • Inspect any scars or striae, the shape and contour of the abdomen, and the fundal height. Purplish striae and linea nigra are normal in pregnancy. The shape and contour may indicate pregnancy size • Palpate the abdomen for: • Organs or masses. The mass of pregnancy is expected. Fetal movements. These can usually be felt by the examiner after 24 weeks (and by the mother at 18–20 weeks). • Uterine contractility. The uterus contracts irregularly after 12 weeks and often in response to palpation during the third trimester. The abdomen then feels tense or firm to the examiner, and it is difficult to feel fetal parts.
Measure the fundal height with a tape measure if the woman is more than 20 weeks’ pregnant. Holding the tape as illustrated and following the midline of the abdomen, measure from the top of the symphysis pubis to the top of the uterine fundus. After 20 weeks, measurement in centimeters should roughly equal the weeks of gestation.
• Auscultate the fetal heart, noting its rate (FHR), location, and rhythm.
• Use either: • A doptone, with which the FHR is audible after 12 weeks, or A fetoscope, with which it is audible after 18 weeks.
• The rate is usually in the 160s during early pregnancy, and then slows to the 120s to 140s near term. After 32 to 34 weeks, the FHR should increase with fetal movement
The location of the audible FHR is in the midline of the lower abdomen from 12 to 18 weeks of gestation. After 28 weeks, the fetal heart is heard best over the fetal back or chest. The location of the FHR then depends on how the fetus is positioned. Palpating the fetal head and back helps you identify where to listen.
• If the fetus is head down with the back on the woman’s left side, the FHR is heard best in the lower left quadrant. If the fetal head is under the xiphoid process (breech presentation) with the back on the right, the FHR is heard in the upper right quadrant.
Genitalia, Anus, and Rectum
• Inspect the external genitalia, noting the hair distribution, the color, and any scars.
Special Techniques
MODIFIED LEOPOLD’S MANEUVERS
• These maneuvers are important adjuncts to palpation of the pregnant abdomen beginning at 28 weeks of gestation. They help determine where the fetus is lying in relation to the woman’s back (longitudinal or transverse), what end of the fetus is presenting at the pelvic inlet (head or buttocks), where the fetal back is located, how far the presenting part of the fetus has descended into the maternal pelvis, and the estimated weight of the fetus.
• This information is necessary to assess the adequacy of fetal growth and the probability of successful vaginal birth
First Maneuver (Upper Pole). Stand at the woman’s side facing her head. Keeping the fingers of both examining hands together, palpate gently with the fingertips to determine what part of the fetus is in the upper pole of the uterine fundus.
Second Maneuver (Sides of the Maternal Abdomen). • Place one hand on each side of the woman’s abdomen, aiming to capture the body of the fetus between them. Use one hand to steady the uterus and the other to palpate the fetus.
Third Maneuver (Lower Pole). • Turn and face the woman’s feet. Using the flat palmar surfaces of the fingers of both hands and, at the start, touching the fingertips together, palpate the area just above the symphysis pubis. Note whether the hands diverge with downward pressure or stay together. This tells you whether or not the presenting part of the fetus, head or buttocks, is descending into the pelvic inlet. If the presenting fetal part is descending, palpate its texture and firmness. If not, gently move your hands up the lower abdomen and capture the presenting part between your hands.
Fourth Maneuver (Confirmation of the Presenting Part). With your dominant hand grasp the part of the fetus in the lower pole, and with your nondominant hand, the part of the fetus in the upper pole. With this maneuver, you may be able to distinguish between the head and the buttocks